Pregnancy
Test
|
Mode of
Action:
|
|
|
|
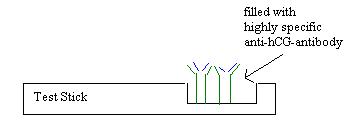
Test
Stick filled with anti-hCG-antibody
from
one B-Cell.
hCG =
human Chorionic Gonadotropin
|
|
|
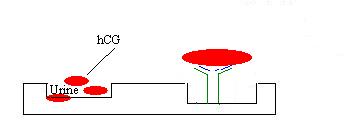
The hCG
in the Urine binds to the antibody.
|
|
|
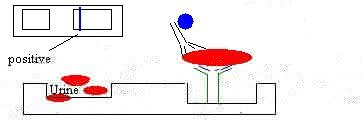
A
second antibody (with a coloured marker) binds to the hCG (but to
a different sub-structure).
|
|
|
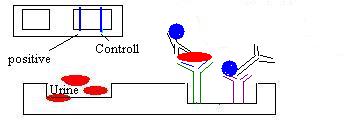
To
see the control line there is a third antibody who binds to the
second antibody.
|
All
tests currently available to test for the presence of a pregnancy
look for the presence of the beta subunit of hCG in the blood
or urine. They are usually performed after a missed menstruation or
2-3 weeks after ovulation. HCG can be detected in urine or blood
after implantation, which occurs six to twelve days after
fertilization. Some home pregnancy tests claim to detect hCG as early
as 4 days before the next expected period. Quantitative blood (serum
beta) tests can detect hCG levels as low as 1 mIU/mL, while urine
tests have published detection thresholds between 20 and 100 mIU/mL,
depending on the brand. This hormone is released by tropoblastic
tissue in the placenta. In rare cases, it may be produced by a germ
cell tumours, or even other forms of cancer, e.g. lung cancer.
Homework:
Find out, if components (antibodies & antigens) for a selfmade pregnancy test can be ordered.
Contents provided by Christian Beiser et al.



